If you are opening a business, you have likely heard of the EIN or Employer Identification Number. Whether you are a big corporation or a small startup, having an EIN is often the first step in starting your business. But what is it? Why is this necessary? Let us break it down in simple terms.
What Is an EIN?
An EIN is similar to a Social Security number (SSN) for businesses. It is a nine-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to identify your business for tax purposes. It is, in other words, your business’s ID number.
The format looks like this: XX-XXXXXX. That number helps the IRS monitor businesses and ensure their tax compliance.
Why Do You Need an EIN?
There are tons of reasons why businesses need to have an Employer Identification Number. Below are the key ones:
- Hiring Employees: If your business has employees, you are required to have an EIN for payroll and tax reporting purposes.
- Tax Reporting: You will need an EIN to file federal taxes, including employment, excise, or alcohol, tobacco, and firearms taxes.
- Opening Bank Accounts: Most banks require an EIN to open a business bank account.
- Applying for Business Credit: You will need an EIN to apply for loans or credit lines in your business’s name.
- Operating as Certain Business Entities: If your business is a corporation, partnership, or LLC, you must have an EIN.
- Compliance with Other Laws: You will need an EIN if you withhold taxes for non-resident aliens or manage retirement plans like Keogh plans.
Who Needs an EIN?
You may be wondering, “Does my business need an Employer Identification Number?” Well, here is a simple checklist:
- You file tax returns for employment, excise, or other specific purposes.
- You withhold taxes for non-wage income paid to non-residents.
- You manage retirement plans like a Keogh.
- Your business is a non-profit, trust, or estate.
Even if your business does not strictly need an EIN (e.g., you are a sole proprietor with no employees), having one can still be a good idea. It allows you to separate your personal and business finances, adding an extra layer of protection against identity theft.
How to Apply for an EIN
The good news is that applying for an EIN is free and straightforward. Here is how you can do it:
Online Application
- The fastest way to get an EIN is by applying online through the IRS website.
- If all information is valid, you will receive your Employer Identification Number immediately.
Note: Online applications are available only for businesses based in the U.S. or its territories.
By Fax or Mail
- Download and complete Form SS-4 from the IRS website.
- Fax the completed form to the IRS and receive your EIN in about one week.
- If you would like to mail it, the turnaround time is about four to five weeks.
- Over the Phone
- If you are outside the United States but require an EIN, you can contact the IRS and apply by phone.
What Information Do You Need to Apply?
You will need to provide:
- Name of your business or entity.
- Name and taxpayer identification number of the responsible person, typically the owner or principal officer.
- The purpose for obtaining (for example, opening a new business).
- The nature of the business (LLC, corporation, partnership, etc.).
- When the business was opened or acquired.
- The main business activity or industry of your business.
Advantages of Having an EIN
An EIN is more than just a way to maintain tax compliance. Here are some additional benefits:
Separates Personal and Business Finances
Using an EIN instead of your SSN keeps your personal information from being stolen for identity theft.
Establishes Business Credit
An EIN is necessary for establishing credit in your business’s name. This can help you qualify for loans, credit cards, or financing in the future.
Simplifies Business Operations
Having an Employer Identification Number makes running your business more professional and efficient, from hiring employees to opening a bank account.
Never Expires
EINs are permanent and unique. Even if your business closes or changes, the number stays attached to your entity forever.
EIN vs. TIN: What is the Difference?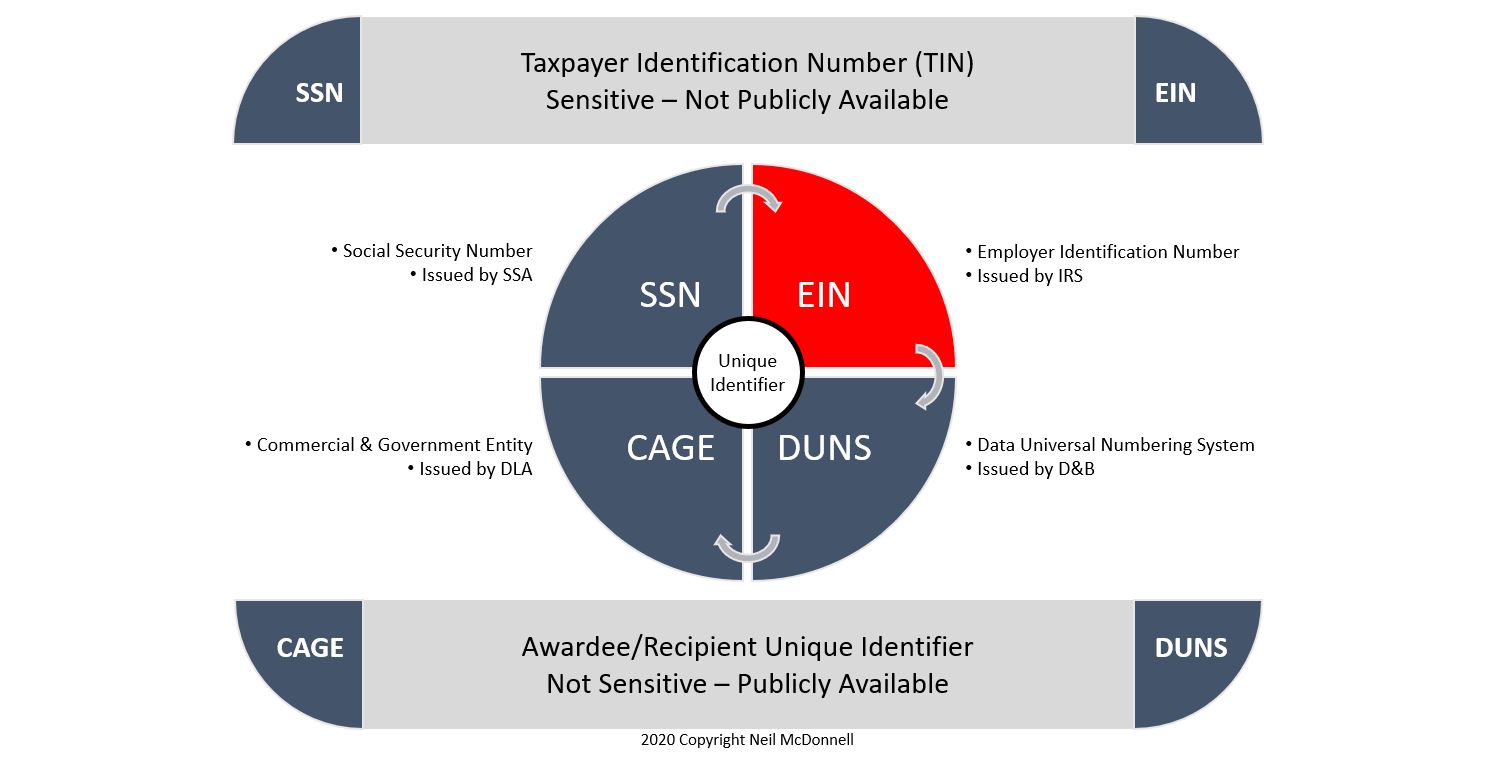
A Taxpayer Identification Number is a general term that encompasses various types of tax IDs. An EIN is but one example of a TIN. There are others:
- SSN (Social Security Number): For people
- ITIN (Individual Taxpayer Identification Number): For aliens not eligible for an SSN, such as aliens who are not residents.
- PTIN (Preparer Taxpayer Identification Number): For tax preparers.
- For most businesses, the EIN is the TIN used to identify them with the IRS.
What if you Lose Your EIN?
In case you lost your EIN, here is what to do: do not panic! Here are some steps to retrieve it:
- Look at the notice issued by the IRS when you obtained your EIN.
- Review your past tax returns.
- Call your bank or other creditors. They might have it on file for you.
- Call the IRS Business & Specialty Tax Line for support.
Closing or Changing Your EIN
Your EIN is for life, but there may come a time when things get to change. Consider these changes that require opening up a new EIN, for example:
- Reversion from a sole proprietorship to a corporation
- Large changes in ownership
- The birth of a new entity
If your business is never going to move, you can close with the IRS, which keeps the EIN active.
Conclusion
An EIN is a crucial component of running a business. It is your business’s identity for tax and financial purposes. Whether hiring employees, opening a bank account, or applying for credit, an EIN is often the key.
Getting one is simple, free, and necessary for most businesses. Even if not required, having an EIN can protect personal information and streamline operations.
